What Is Metal Stamping And What Are Its Design Principles?
- Metal Stamping |
- Jan 2, 2023
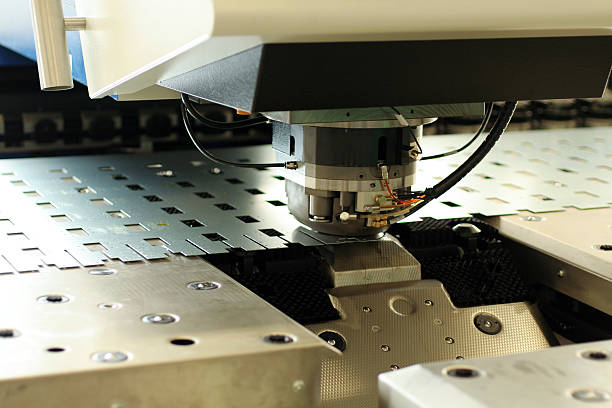
The average individual may not realize it, but metal stamping is a vital aspect of the production process. It gives numerous benefits to different industries and businesses all over the world. Metal stamping is a simple yet versatile production technology. Innovators have refined and enhanced it throughout time to produce the incredibly efficient methods now employed. Metal stamping is a low-cost, high-speed stamping manufacturing method that produces many identical metal components. With that in mind, here’s more information about metal stamping and how it works.
What Is Metal Stamping?
Sheet Metal stamping, also called pressing, is a process, inserting flat sheet metal into a stamping press. It is a complicated procedure that can involve a variety of metal forming processes. It can either be in coil or blank form. A tool and die surface molds the metal into the required shape in the press. Stamping techniques used to form metal include:
- Embossing
- Punching
- Bending
- Blanking
- Flanging
- Coining
Discover Automotive Metal Stamping Process
Metal Stamping Manufacturing Process
The metal stamping process starts by getting the raw metal ready. This is usually sheet metal or metal coils. The metal is cut, trimmed, and flattened so it has the right size and smoothness for stamping. Metal pressing is an essential to generating inexpensive and well-crafted parts and components in various industries. These industries range from automotive and aerospace to medical and electronics.
Feeding
Once the sheet metal is prepared, the metal pieces are fed into a stamping press. Most factories use automatic feeders to place the metal correctly each time.
Stamping
A die presses into or through the metal with a very high force. This shapes the metal or cuts it according to the die design.
Forming and Cutting
Different forming actions can happen during this step, depending on what part is being made:
Blanking: Blanking is the process of cutting out the outer shape of the part from the sheet.
Punching: Metal punching is a fabrication method where the punch enters the punching die and extracts a scrap slug from the workpiece
Bending: Bending is a technique for deforming metal into L, U, or V-shaped profiles. Mechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic, and CNC press braking are the many types.
Coining: Coining is a metal-bending process in which a die and a punch press stamp the item between them.
Embossing: Embossing creates a raised design by pressing a sheet against the die in the shape of the desired pattern. When the metal goes into an embossing machine, a tool raises the other side of the blank.
Flanging: This method is used when the edge of the sheet metal part needs to be turned upward or outward. Special tools help form this rim cleanly.
Part Removal
After the shaping is done, the part is taken out of the press. Simple parts can be made in one press stroke. More complex designs may need several steps or a progressive die that performs different actions in sequence.
Post-Processing
Once stamping is complete, the part may need extra work like cleaning, trimming, or smoothing the edges. Stamping is done without heat, but the metal can feel warm because of friction during the process.
Also Read- Automotive Stamping Dies Save Big With Metal Stamping
Principles of metal stamping design
In general, you should avoid overly narrow projections in stamped items. This is because they easily become warped and affect the perception of quality in the finished product. Designs should, whenever possible, stem from using existing dies for common forms and bends. The requirement to design a specialized die for stamping will raise the initial tooling expenses.
You can handle some challenges with creative tool design, while others cannot. For example, some stamping designs that satisfy all of the dimensional criteria is nearly impossible. This shoddy design for manufacturability might lead to excessive maintenance and scrap expenses. Production requires constant changes and service, resulting in an extremely inefficient program.
Metal stamping is a cost-effective method of making large quantities of parts with various features. These features include strength, durability, good conducting properties, and stability. Here are some metal stamping design guidelines that can help you create a product that uses all the benefits of the metal stamping process.
1. You must develop metal stamping components to meet product and technical performance requirements.
2. Under typical use conditions, designed metal stamping parts aim to reduce the dimensional accuracy grade and surface roughness grade requirements. It is helpful to:
- Product interchange
- Waste reduction
- Product quality stability
3. The design of stamping components must be conducive to improving the following:
- Use of metal materials
- Reducing the variety and specifications of materials
- Reducing material consumption as much as possible
Utilise low-cost materials as much as possible to minimise waste and reduce scrap.
4. The design of precision stamping parts must be simple in shape and reasonable in structure. This is to help simplify the mold structure and simplify the number of processes, i.e.,
- The one with the fewest, simplest stamping process to complete the parts processing
- Reduce the use of other processing methods
- Conducive to stamping operation
All this is aimed at organising the realisation of mechanisation and automation in production, and to improve labour productivity.
5. The planned metal stamping components should process current equipment, process equipment as feasible, and assist in die service life extension.
Applications of Metal Stamping Across Industries
One of the best things about metal stamping is that it can be utilised in so many different ways. Many businesses utilise this approach to build parts that are cheap, endure a long time, and are easy to make again.
Automotive metal stamping is arguably the most common use of this technology in the car industry. A common approach to creating body panels, bracing, frames, and engine parts for cars is to stamp them. Automotive metal stamping makes cars light, safe, and it works the same way every time.
In electronics, being right is the most important thing. Parts for connectors, terminals, and circuits are stamped to precise standards so that they may be used with anything from smartphones to heavy machinery.
Aerospace: Things need to be sturdy and trustworthy in planes and space exploration. Because they can keep tough even in bad weather, stamped metal parts are particularly frequent.
Tools, appliances, and building supplies are some of the things we use every day that need stamped parts. This technology lets you produce strong parts that are also cheap, which makes it possible to make a lot of them.
Metal stamping can be utilised in many ways, and it can make things that are better than what you might think. The method is now a significant aspect of modern production because it is cheap and works well.
Also Read- Benefits of Using Combination Die For Your Metal Stamping Project
Stamping designs are quite robust and cost-effective when the product designer consults with the parts manufacturers. When the manufacturing and component design teams collaborate, the result is the optimal production design—and often a component stamping cost savings of up to 50%. A well-thought-out design for manufacturability, thoroughly assessed by both the component design and manufacturing teams, will result in the highest-quality stamped part at the lowest cost. That’s in everyone’s best interests.
FAQs
Q1. What materials are used in metal stamping?
Some of the most prevalent materials are steel, aluminium, brass, copper, and titanium. The choice depends on how strong, conductive, and long-lasting the ultimate product needs to be.
Q2. What is the purpose of sheet metal stamping?
The main goal is to use flat sheets of metal to manufacture finished goods that are strong, cheap, and very precise. It makes sure that manufacturing a lot of things doesn’t harm the quality.
Q3. What industries use production metal stamping?
Many different sectors use production metal stamping to create critical parts. These fields include autos, planes, electronics, construction, and consumer products.
Q4. How to choose a sheet metal stamping manufacturer?
Pick a business that has a lot of experience, current stamping machines, quality certificates, and the ability to create a lot of goods while yet preserving strict quality control.
Ujjwal handles crucial roles like AGM Marketing, researcher, and is an author for KDDL – Eigen. He currently works with Eigen for implementing proven techniques and strategies for marketing plans on online and offline platforms. An expert in efficiently executing SEO, SEM, email marketing, social media marketing, PR marketing, Print campaigns, etc. Ujjwal has coordinated an efficient marketing team on various creative campaigns and programmatic buying to support various digital cross-promotion efforts. Implement efficient search optimization strategies with the help of collateral material and metrics.
In his former years, Ujjwal has years of experience in a managerial role for several reputed companies. His years of experience combined with the flair of writing help him come up with result oriented strategies for Eigen.